Introduction :As an essential product in modern infant care, diapers have always been a focus for parents and the infant care industry due to their comfort, absorbency, and convenience. With the advancement of technology and the rise in consumer demand, the manufacturing process of diapers is continuously innovating and improving. This article aims to provide a comprehensive perspective for diaper retailers, wholesalers, and manufacturers to deeply understand the manufacturing process and production methods of diapers, and how they meet market demands.
The Evolution of Diapers
The history of diapers can be traced back to the 1940s when the concept of disposable diapers was first introduced. Over time, the design and materials of diapers have undergone multiple innovations to improve their absorbency, breathability, and comfort. Modern diapers are typically composed of multiple layers of materials, including a surface layer, an absorbent core, and a leak-proof layer, to ensure the baby's dryness and comfort.
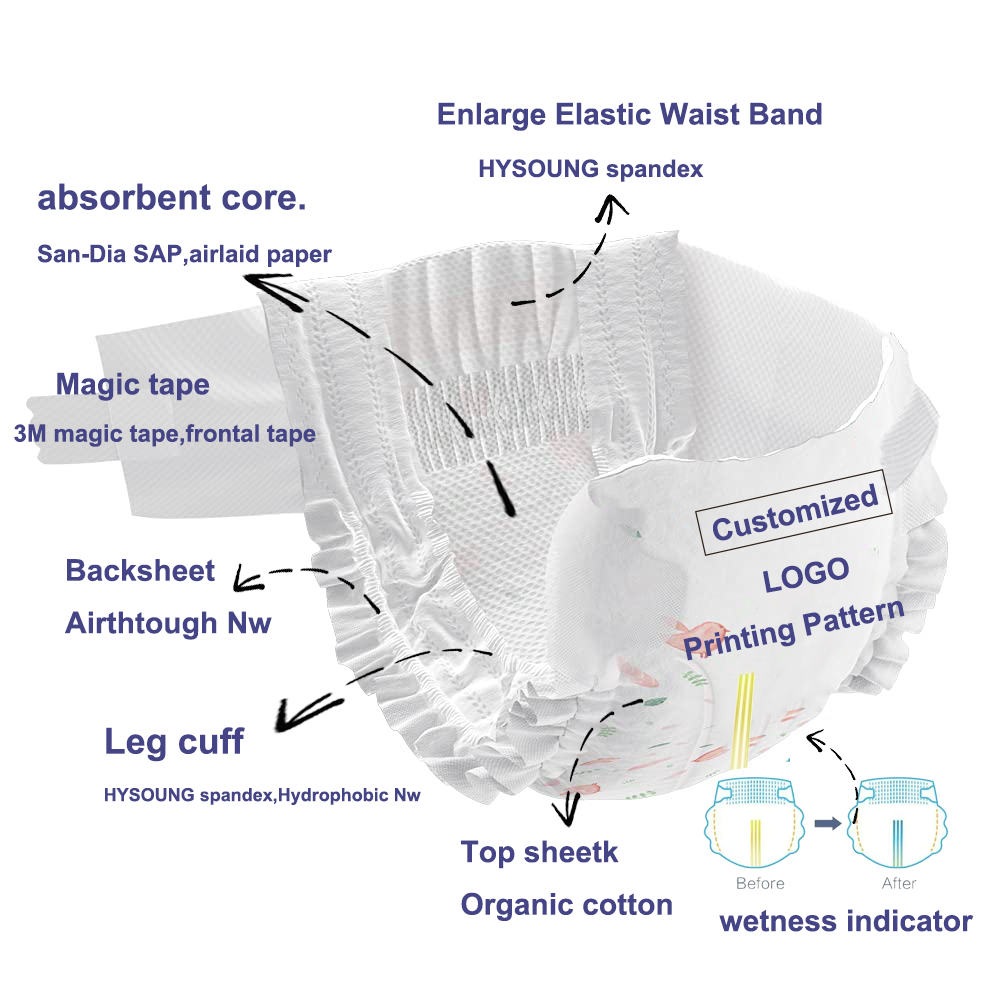
Basic Structure of Diapers
1. **Surface Layer**: The outer layer that directly contacts the baby's skin, usually made of soft non-woven fabric to provide a comfortable touch.
2. **Absorbent Core**: The core part of the diaper, composed of super absorbent polymer (SAP) and pulp fibers, capable of quickly absorbing and locking in urine.
3. **Leak-Proof Layer**: Located at the edges of the diaper, usually made of plastic or elastic materials to prevent urine leakage.
Manufacturing Process
Material Preparation
1. **Non-Woven Fabric**: Made through processes such as melt-blowing, spunbonding, or hydroentanglement, used for the surface layer and leak-proof layer.
2. **Super Absorbent Polymer (SAP)**: Prepared through polymerization reactions, with extremely high water absorption capacity.
3. **Pulp Fibers**: As part of the absorbent core, providing structural support.
Manufacturing Process
1. **Core Preparation**: Mix SAP and pulp fibers to form the absorbent core.
2. **Shaping**: Place the absorbent core between non-woven fabrics to form the basic structure of the diaper.
3. **Cutting and Folding**: Cut the diaper into the appropriate size according to design requirements and fold it.
4. **Edge Treatment**: Add the leak-proof layer and seal the edges using heat sealing or ultrasonic welding to ensure the sealing of the edges.
5. **Packaging**: Sterilize the finished diapers, package them, and prepare them for shipment.
Quality Control and Innovation
To ensure the quality and performance of diapers, manufacturers need to conduct strict quality control, including material testing, production process monitoring, and finished product inspection. In addition, innovation is key to driving industry development, such as developing more environmentally friendly materials, improving absorption efficiency, and developing smart diapers.
Conclusion
The manufacturing process of diapers is a complex and delicate process involving a variety of materials and multiple processes. With the continuous advancement of technology, we can expect diapers to be more comfortable, environmentally friendly, and intelligent in the future. For retailers, wholesalers, and manufacturers, understanding these manufacturing processes and innovation trends will help them better meet market demands and provide higher quality products and services.
## References
1. "Disposable Diaper Technology: An Overview" by Smith, J. (2023)
2. "Innovations in Absorbent Core Technology" by Lee, M. (2022)
3. "Sustainability in Diaper Manufacturing" by Green, A. (2024)
 Hot News
Hot News2024-09-06
2024-09-06
2024-09-06
2024-09-06
2024-09-06
2024-07-17